TEL’s Kehati Park Continues to Improve
The TEL Biodiversity Park is continuously improving its efforts to sustainably preserve the diversity of endemic/local flora and fauna. In alignment with its vision and mission, the establishment of this biodiversity park aims to function as a conservation area for a collection of various local plants and animals, serving as a source for seeds and plant seedlings, as well as contributing to environmental preservation.
Why Build a Nursery for Biodiversity Park?
The journal titled “What Are the Benefits of Plants Indoors and Why Do We Respond Positively to Them?” outlines the various benefits we can gain from plants in our environment. By planting and providing a variety of vegetation, the air quality in our surroundings can be well-maintained, as plants are capable of producing oxygen. Additionally, plants release water vapor, which can enhance the relative humidity in the areas where we live.
TPlants can influence a person’s feelings and emotions when viewed. Studies have shown that for individuals who work extensively in front of a computer, observing plants can help improve focus. The presence of plants around us has also been proven to reduce stress and promote relaxation.
From this explanation, we can conclude that preserving plants brings numerous benefits to both the environment and ourselves. Let us work together to maintain the preservation of nature and biodiversity on this Earth we inhabit.
Building a Biodiversity Park Offers Several Advantages, Including:
- For the Community: It serves as a means of learning and economic empowerment, a tourist attraction, educational opportunities, knowledge enhancement, and increased environmental awareness.
- For the Environment: It helps preserve local biodiversity that is becoming increasingly rare and endangered, and provides a habitat for wildlife displaced by industry and urban development.
- For the Company: It is an effort to obtain PROPER (Corporate Performance Rating in Environmental Management) recognition.
- For the Government: It enhances the performance of relevant ministries or institutions.
The Biodiversity Park Provides Various Benefits, Including:
- It serves as a breeding ground for plants and animals that supports ecosystem preservation and benefits humanity.
- It supplies seedlings of various plants that are becoming scarce.
- It acts as a genetic resource for plants and local vegetation that are currently hard to find and threatened with extinction.
- It serves as a research facility, particularly related to the conservation of rare plants and animals and fosters the development of new knowledge beneficial to society.
- It provides superior seeds and seedlings for agricultural development in the surrounding area.
It creates green open spaces that can improve the microclimate, offering shade, coolness, natural beauty, and comfort for both the company and the local community. - It increases vegetation cover, which plays a crucial role in improving the hydrological system by enhancing water catchment areas or reservoirs, preventing erosion and landslides, and providing habitat for various species.
Biodiversity plays a significant role and contributes to the company’s assets, particularly in the preservation of flora and fauna, while maintaining biodiversity as a capital asset for regional and sustainable development efforts.
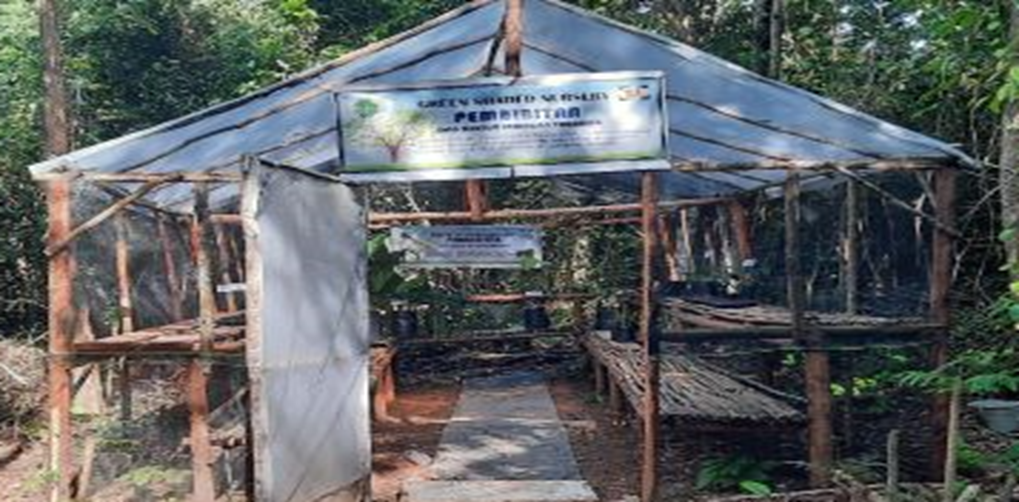
Facilitating the Biodiversity Park is a mandatory activity for developing the park’s infrastructure. This commitment is part of PT Tanjungenim Lestari Pulp and Paper’s dedication to establishing the TEL Biodiversity Park in the PT. TEL area, Banuayu Village, Muara Enim District. One essential infrastructure component of the Biodiversity Park is the establishment of a Nursery.
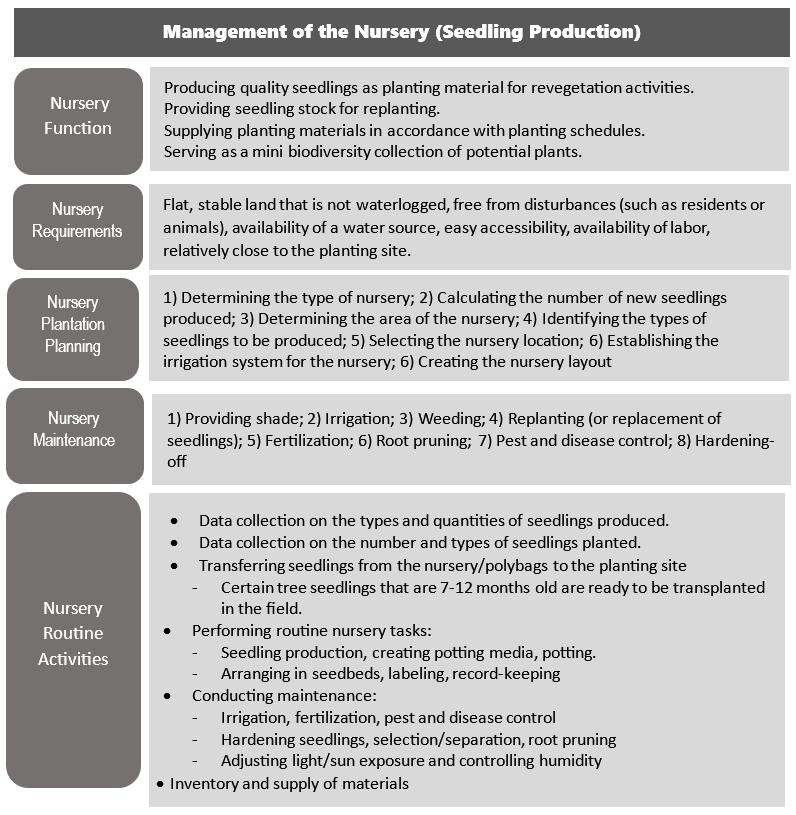
Development of a Nursery for Seedling Production at the TEL Biodiversity Park
A nursery is an area of land utilized for producing specific tree seedlings that meet general requirements regarding size and quality, making them suitable for planting in the field.

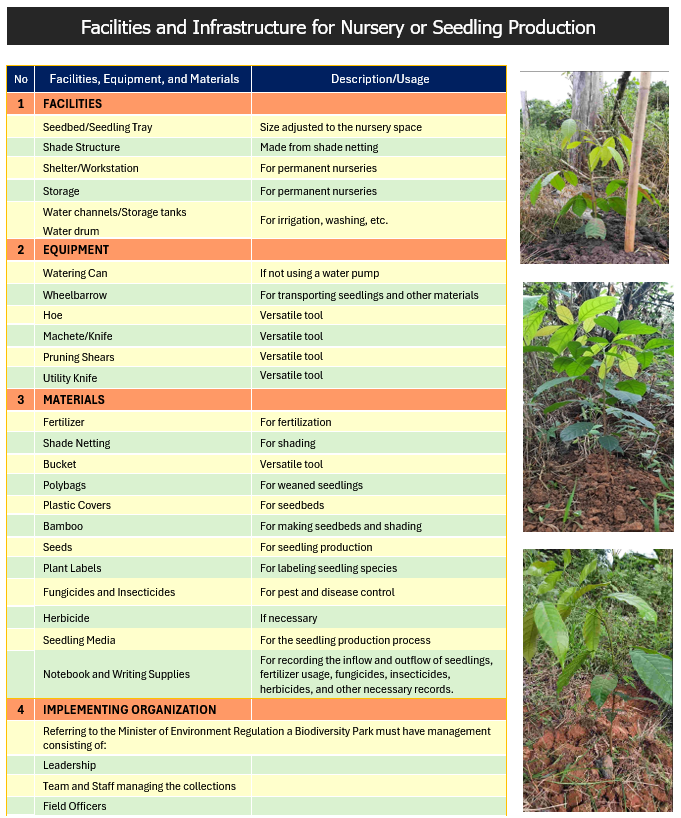
The Biodiversity Park Features a Nursery (Ref. Minister of Environment and Forestry Regulation). The nursery is intended to prepare seedlings for planting and for replanting in the Biodiversity Park. The nursery can also be utilized to produce tree seedlings for distribution to the surrounding community.
The construction of the nursery at the TEL Biodiversity Park is carried out in a technical and straightforward manner, involving local community members, using a semi-open model with UV plastic roofing and shade netting.
In accordance with the Strategic Plan for the TEL Biodiversity Park, this simply constructed nursery will function as a model agricultural plant nursery, integrating staple crops with various endemic and productive plant species (IUCN status: VU-LC & NE) that provide diverse benefits.
The Biodiversity Park is designed to serve as an observation area for flora and fauna, as well as a nursery for plant collections, breeding, genetic resources, and seed sources. It is hoped that in the long term, the TEL Biodiversity Park can serve as a center for scientific development and education, outreach, a nature tourism destination, and a green open space that can provide economic value to the surrounding community.
The establishment of the TEL Biodiversity Park will enhance the existing flora and fauna in the company’s location, beginning with a seedling program to increase the variety of endemic/local trees, fruit trees, and various local timber species. This effort aims to support wildlife conservation by providing new habitats for animals and a source of food from the plants within the Biodiversity Park


Types of Plant Seedling Production that Have Been Implemented which is specifically planted in the tropical fruit garden project area – Biodiversity Park of Tel :
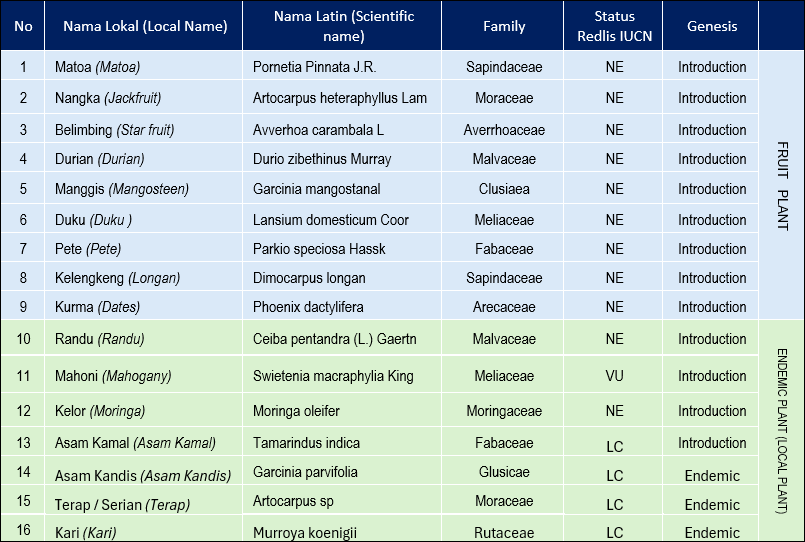
There are several local tree species with important value indices at the TEL Biodiversity Park, such as the Asam Kandis tree and the Terap/Serian tree, as well as other significant species currently being cultivated at the TEL Nursery, including Mahoni and Matoa trees. Both species possess a higher capacity for carbon dioxide absorption compared to other plants.